Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most prevalent diseases affecting people of all ages — from neonatal to the elderly. Every year about 150 million people are diagnosed with urinary tract infections worldwide. It is estimated that women have a lifetime risk of developing UTI of 60%; in contrast, men have a lifetime risk of only 13%.
Though common, a majority of people — women in particular — are unaware of the causes, symptoms, and management of urinary tract infections.
In the following article, we’ll cover what urinary tract infection is, its causes, different UTI symptoms, prevention, and management.
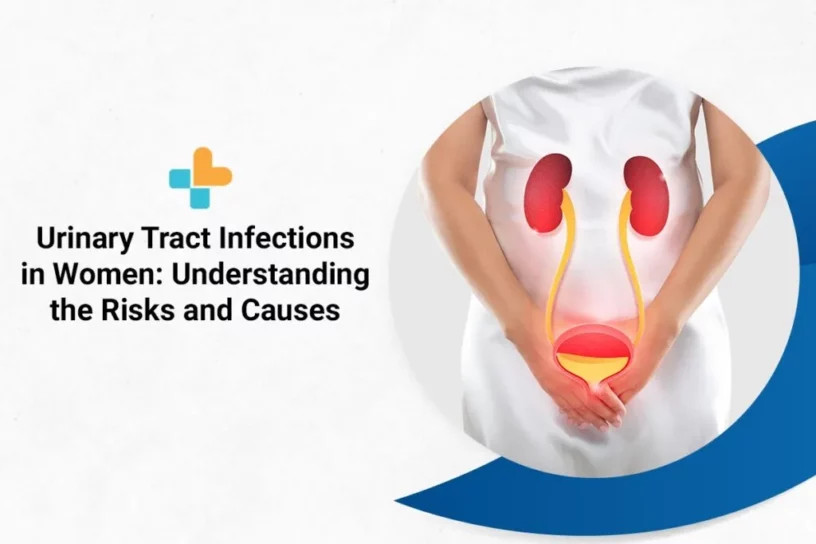
What Is the Urinary Tract?
The urinary tract is a group of organs that work together to produce, store, and excrete urine from the body. It includes the following organs:
- Kidneys: These are small organs that filter waste and water and remove it from the body in the form of urine.
- Ureters: These thin tubes transport urine from the kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like container that stores urine.
- Urethra: This tube excretes urine stored in the bladder.
What Is Urinary Tract Infection?
Urinary tract infection is an infection that occurs when small, disease-causing germs (microbes) — such as viruses, fungi, or bacteria — enter the body to disrupt the functioning of the urinary tract.
A urinary tract infection can occur in any part of the urinary system. The lower urinary tract (bladder and urethra) is more vulnerable and susceptible to it as a female’s urethra is shorter, making it easier for the bacteria to reach the bladder.
What Causes Urinary Tract Infections?
The Urology Care Foundation reports that different bacterias exist on or around the rectum and vagina. When these bacterias enter the urethra, they can travel to the bladder and cause urinary tract infections.
The female urethra is shorter and closer to the anus, which makes it possible for faecal flora like E. coli to easily reach the bladder and create an imbalance in the urinary system, leading to urinary tract infections.
Risk Factors That Can Cause UTI
Though bacteria entering the urethra is a common cause, there are other risk factors that can contribute to urinary tract infections. These include the following:
- Sexual activity
- Urinary tract blockage (kidney stones)
- Menopause (decreased levels of estrogen)
- Certain medical conditions like diabetes
- Long-term use of urinary catheters
- Weakened immune system
- Unhygienic intimate care practices
What Are the Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections?
An infection of the urinary tract causes inflammation in the lining resulting in the following UTI symptoms:
- Pain in the abdomen, back or pelvic area
- Constant pressure in the pelvic floor
- Frequent and urgent need to urinate (increasingly at night)
- Incontinence (urine leakage)
- Painful and burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy, dark, bloody, or strong-smelling urine
- Painful sexual intercourse
If the infection reaches the upper urinary tract (kidney), then more severe symptoms may occur, such as high fever and chills, nausea, vomiting, and severe pain in the pelvic region. In such cases, you need to schedule a doctor’s visit at the earliest and get a proper diagnosis.
Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosis
A general practitioner may diagnose infection based on the reported UTI symptoms, medical history, and test results.
Here are some of the common methods used to diagnose UTIs:
- Urinalysis: An uncontaminated urine sample is analyzed in a lab to check for white blood cells, red blood cells, and bacteria that are signs of infection and helps doctors determine the best course of action.
- Urine culture: A urine sample is sent to a laboratory to grow any bacteria found in the urine. The test helps identify bacteria that are causing the infection and evaluate effective medication.
- Diagnostic imaging: In case of chronic UTIs and structural problems in the urinary tract, diagnostic procedures such as cystoscopy, CT scans, MRI scanning, ultrasound, radiation tracking, and X-rays may be used to assess the urinary tract.
Treatment for Urinary Tract Infections in Women
The treatment for urinary tract infections in women depends on the severity of the condition and the type of bacteria causing them. The most common options used in treating urinary tract infections are as follows.
1. Antibiotics
Antibiotics are medicines that kill bacteria causing UTIs. These are the first line of treatment for simple urinary tract infections. Your doctor will choose an antibiotic based on your urine culture and test results. Nitrofurantoin, amoxicillin, doxycycline and ciprofloxacin are some of the most commonly used antibiotics in treating UTIs.
2. Pain Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help relieve discomfort and pain for a brief period. But, we strictly advise getting a prescription medication, as pain in the pelvic region can mean something more than just UTI.
3. Increased Fluid Intake
Drinking plenty of water can help flush bacteria from your urinary tract. It helps in managing UTI symptoms and reduces discomfort in simple cases of urinary tract infections.
Prevention
Keeping yourself hydrated and maintaining a good intimate hygiene regime can help subside the symptoms. But in any case, visiting an expert health practitioner who can provide the right treatment at the right time is always recommended.
And although there are no foolproof ways of avoiding a UTI, following lifestyle changes go a long way in helping one manage and prevent UTI, bladder infection or kidney infection.
- Practice good hygiene: Wiping front to back after using the washroom, taking showers instead of baths, and urinating after sex can help prevent bacterial spread.
- Avoid irritants: Feminine products such as soaps, douches, powders, and sprays can increase the risk of UTIs.
- Urinate frequently: Don’t hold in urine for long periods of time, as this can allow bacteria to multiply.
- Wear breathable clothing: Tight clothing and lingerie can trap moisture and bacteria, increasing the risk of UTIs.
Stay Safe From Urinary Tract Infections
A diet high in sugar and processed foods can increase the risk of UTIs, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports a healthy one. Additionally, cranberry supplements are also believed to help prevent UTIs.
If you think you have UTI symptoms and want to further avoid the risk of bladder infections or kidney infections, we advise you to visit a reputed healthcare centre, likeAyu Health, and get relevant tests done for quick medical attention.
If you’d like to learn more about urinary tract infections and their treatment, or if you seek medical intervention, get in touch with Ayu Health at +91 636-610-0800 or book an appointment on our website.
Our Hospital Locations
General Surgery Hospitals in Chandigarh | General Surgery Hospitals in Bangalore | General Surgery Hospitals in Jaipur | General Surgery Hospitals in NCR | General Surgery Hospitals in Hyderabad
Our Doctors
General Surgery Doctors in Chandigarh | General Surgery Doctors in Bangalore | General Surgery Doctors in Jaipur | General Surgery Doctors in NCR | General Surgery Doctors in Hyderabad
About the Author

Dr. S. Goel
Dr. S. Goel is a renowned Internal Medicine Specialist currently practicing at Ayu Health, Bangalore. He is a Specialist in Internal Medicine, Diabetes HTN, Paediatric Care, and Family Medicine.